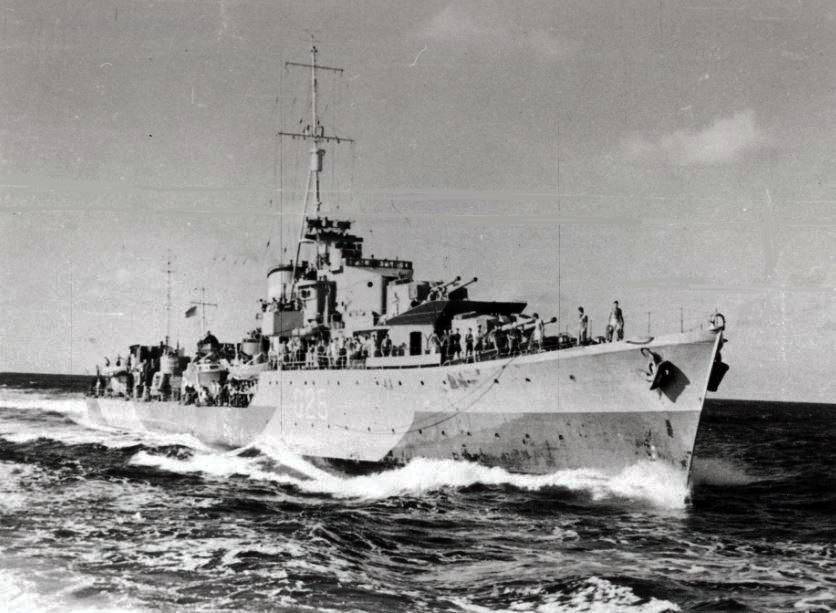
Difference between revisions of "HMAS Nepal"
From Our Contribution
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
==Remarks== | ==Remarks== | ||
| − | Nepal commissioned on 11 May 1942 | + | Nepal commissioned on 11 May 1942as the last of the Australian N Class destroyers to commission and began her war service with the Home Fleet at Scapa Flow. In June 1942 she returned to her builders yards at Southampton for docking in preparation for her movement to the Indian Ocean. |
| − | |||
| − | + | In July 1942 she sailed from Glasgow for Kilindini where she joined her sister ships ''Napier, Norman'' and ''Nizam'' as a unit of the Eastern Fleet, on escort, fleet exercise and patrol duties. In September 1942 ''Nepal'' took part in the second phase of the Madagascar campaign with Vichy forces surrendering on 5 Nov 1942. ''Nepal'' was part of the forces assembled for the capture of Tamatave, Madagascar's chief port. ''Nepal'' spent the closing months of 1942 and the start of 1943 escorting convoys. | |
| − | |||
| − | Nepal | + | On 19 March 1943 she sailed from Durban for Australia. En route she suffered slight damage when a severe cyclone was encountered between Mauritius and Diego Garcia. A refit at Sydney occupied the period of 8 April to 22 May 1943. In June 1943 Nepal returned to Indian Ocean convoy escort and patrol duties.'' Nepal'' remained with the Eastern Fleet through the first seven months of 1944, operating from Trincomalee in Ceylon. In April 1944 she was one of the destroyer screen protecting the carriers ''USS Saratoga'' and ''HMS Illustrious'' for the air strikes against the Japanese held port of Sabang in Sumatra and in May against Surabaya in Java. In August 1944 ''Nepal'' returned to Australian for refit before rejoining the Eastern Fleet on 1 November. |
| − | |||
| − | + | ''Nepal'' was involved in the support of the landing of the Indian 74th Brigade on the Mayer Peninsula, in doing so firing her first shots in anger. The bombardment of Japanese positions continued through the remainder of December, ''Nepal'' alternating with her sister ship ''Napier'' as fire support destroyer, running to Chittagong every third day for stores and ammunition. In January 1945 ''Nepal'' took part in further Burma operations, including the capture of Akyab Island. The Japanese withdrawal turned the planned assault into a routing landing obviating any need for fire support from the sea. On 6 January Nepal left the Burma theatre for docking at Colombo. On 25 Jan 1945 she returned to Burma for the seizure of Cheduba Island by Royal Marines of the Eastern Fleet. There was only minor opposition ashore. Nepal took no part in the bombardment. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | On 1 Feb 1945 Nepal resumed an offensive role in the Burma theatre, shelling Japanese positions on Ramree Island for three days. On 5 February she badly damaged her starboard propeller when she struck a submerged rock in the Kaleindaumg River. However, operating on one engine she remained in the Burma theatre until 12 February. On 1 Mar 1945 ''Nepal's'' World War II service in the Indian Ocean finally ended when she sailed from Trincomalee to join the British Pacific Fleet in Sydney, joinming the British Task Force 57 which participated in the invasion of Okinawa, between March and May 1945. During the closing stages of the Pacific War, ''Nepal'' continued operating as a fleet destroyer with the British Pacific Fleet. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | The period of 7 to 28 Jun 1945 was spent in Sydney, exercising with other ships of the 7th Flotilla at Jervis Bay. In July she rejoined the British Pacific Fleet at sea, and the last day of hostilities found ''Nepal'' at Manus. On 6 Sep 1945 Nepal arrived in Tokyo Bay, four days after the surrender ceremony. She spent five weeks in Japanese waters before returning to Sydney for reversion to the Royal Navy. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | The period of 7 to 28 | ||
| − | |||
| − | On 6 | ||
==Battle Honours== | ==Battle Honours== | ||
Revision as of 13:59, 25 March 2023
Remarks
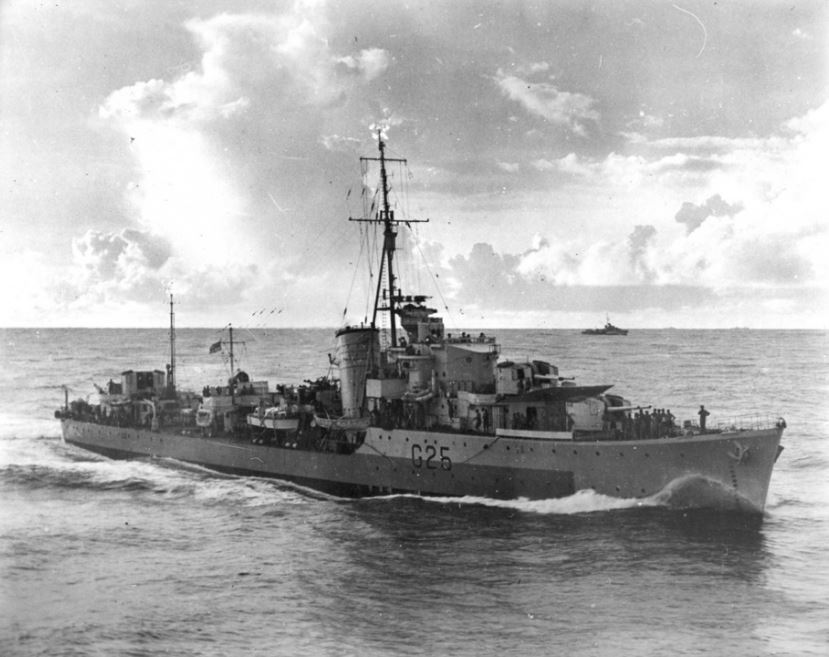
Nepal commissioned on 11 May 1942as the last of the Australian N Class destroyers to commission and began her war service with the Home Fleet at Scapa Flow. In June 1942 she returned to her builders yards at Southampton for docking in preparation for her movement to the Indian Ocean.
In July 1942 she sailed from Glasgow for Kilindini where she joined her sister ships Napier, Norman and Nizam as a unit of the Eastern Fleet, on escort, fleet exercise and patrol duties. In September 1942 Nepal took part in the second phase of the Madagascar campaign with Vichy forces surrendering on 5 Nov 1942. Nepal was part of the forces assembled for the capture of Tamatave, Madagascar's chief port. Nepal spent the closing months of 1942 and the start of 1943 escorting convoys.
On 19 March 1943 she sailed from Durban for Australia. En route she suffered slight damage when a severe cyclone was encountered between Mauritius and Diego Garcia. A refit at Sydney occupied the period of 8 April to 22 May 1943. In June 1943 Nepal returned to Indian Ocean convoy escort and patrol duties. Nepal remained with the Eastern Fleet through the first seven months of 1944, operating from Trincomalee in Ceylon. In April 1944 she was one of the destroyer screen protecting the carriers USS Saratoga and HMS Illustrious for the air strikes against the Japanese held port of Sabang in Sumatra and in May against Surabaya in Java. In August 1944 Nepal returned to Australian for refit before rejoining the Eastern Fleet on 1 November.
Nepal was involved in the support of the landing of the Indian 74th Brigade on the Mayer Peninsula, in doing so firing her first shots in anger. The bombardment of Japanese positions continued through the remainder of December, Nepal alternating with her sister ship Napier as fire support destroyer, running to Chittagong every third day for stores and ammunition. In January 1945 Nepal took part in further Burma operations, including the capture of Akyab Island. The Japanese withdrawal turned the planned assault into a routing landing obviating any need for fire support from the sea. On 6 January Nepal left the Burma theatre for docking at Colombo. On 25 Jan 1945 she returned to Burma for the seizure of Cheduba Island by Royal Marines of the Eastern Fleet. There was only minor opposition ashore. Nepal took no part in the bombardment.
On 1 Feb 1945 Nepal resumed an offensive role in the Burma theatre, shelling Japanese positions on Ramree Island for three days. On 5 February she badly damaged her starboard propeller when she struck a submerged rock in the Kaleindaumg River. However, operating on one engine she remained in the Burma theatre until 12 February. On 1 Mar 1945 Nepal's World War II service in the Indian Ocean finally ended when she sailed from Trincomalee to join the British Pacific Fleet in Sydney, joinming the British Task Force 57 which participated in the invasion of Okinawa, between March and May 1945. During the closing stages of the Pacific War, Nepal continued operating as a fleet destroyer with the British Pacific Fleet.
The period of 7 to 28 Jun 1945 was spent in Sydney, exercising with other ships of the 7th Flotilla at Jervis Bay. In July she rejoined the British Pacific Fleet at sea, and the last day of hostilities found Nepal at Manus. On 6 Sep 1945 Nepal arrived in Tokyo Bay, four days after the surrender ceremony. She spent five weeks in Japanese waters before returning to Sydney for reversion to the Royal Navy.
Battle Honours
- Indian Ocean 1941-45
- Pacific 1941 -45
- Burma 1944 - 45
- Okinawa 1945
Crew
- William Henry Knox 19 Nov 1942 - 4 Apr 1943