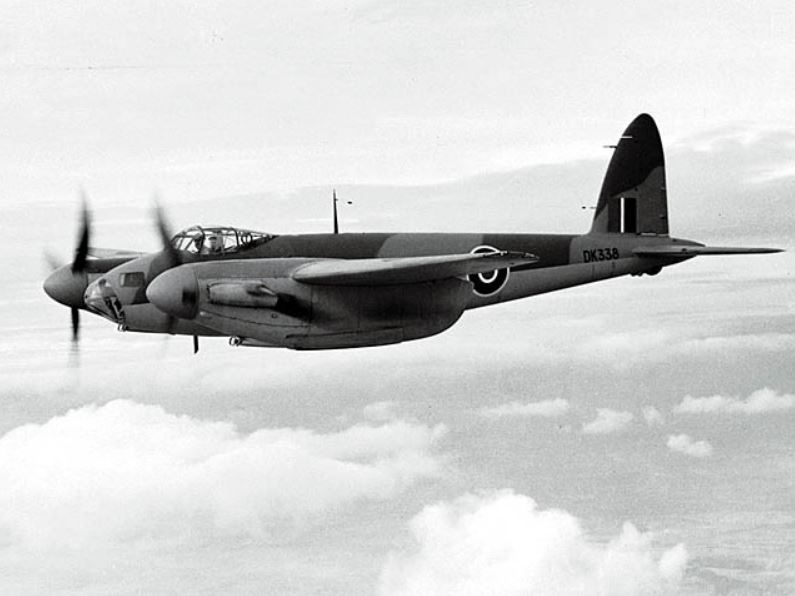
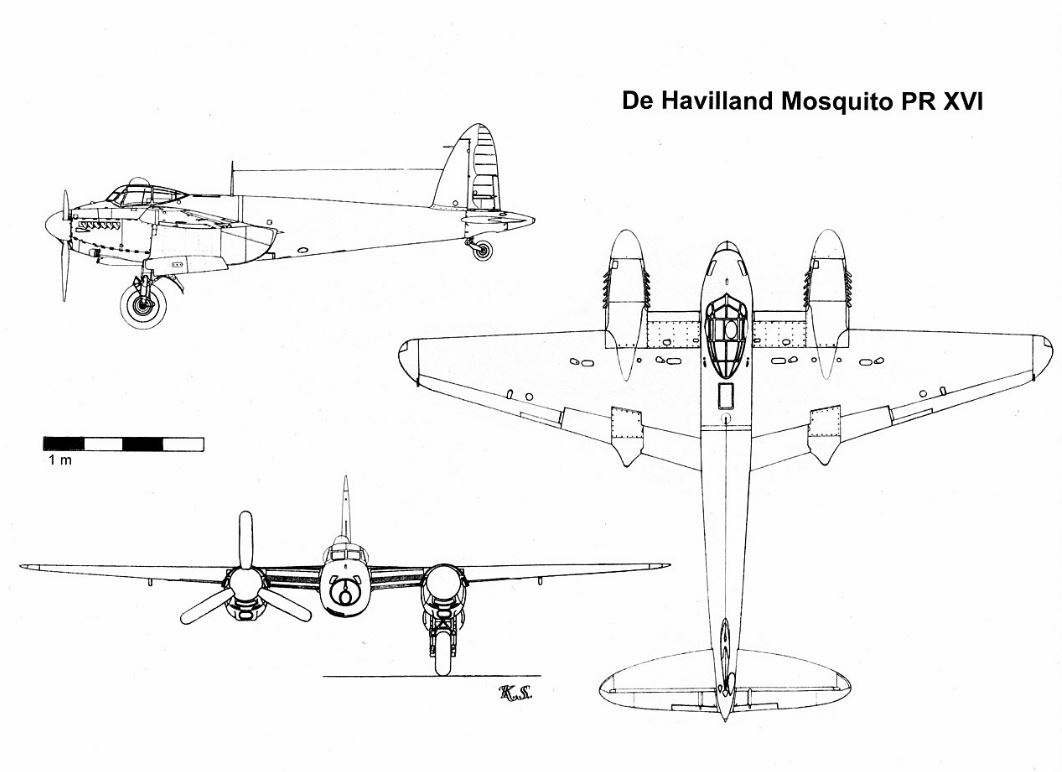
De Havilland Mosquito
From Our Contribution
Revision as of 00:12, 3 February 2020 by Linton (talk | contribs) (Created page with "{{infobox aircraft | image = File:de_Havilland_Mosquito.jpg | caption = | image2 = File:de_Havilland_Mosquito_PR_XVI.jpg | caption2 =...")
Revision as of 00:12, 3 February 2020 by Linton (talk | contribs) (Created page with "{{infobox aircraft | image = File:de_Havilland_Mosquito.jpg | caption = | image2 = File:de_Havilland_Mosquito_PR_XVI.jpg | caption2 =...")
Remarks
Unusual in that the plane was constructed from composite wood. The first prototype flew on 25 Nov 1940, with official trials commencing 19 Feb 1941. Development was delayed when de Havilland were ordered to stop work on it to concentrate on other work on their books. However, development recommenced and during trials it demonstrated that it had a much higher speed than the Supermarine Spitfire. Original design request was for a twin engine medium bomber.
General characteristics
- Crew: Two Pilot, bombardier/navigator
- Length: 13.56 m
- Wingspan: 16.51 m
- Height: 5.31 m
- Empty weight: 6,486 kg
- Max takeoff weight: 11,340 kg
- Powerplant: 2 x Rolls Royce Merlin piston engines
- Maximum speed: 668 Km/h at 8,500 m
- Range: 2,100 km
- Service ceiling: 11,000 m
- Armament
- Guns:
- Bombs:1,800 kg
Crew members
No. 87 Squadron RAAF Ground Crew
- Kevin David Anderson 18 Jan 1945- Feb 1946